Università degli Studi di Pavia - unipv.it
Shape memory engineered scaffold (SMES) for potential repair of neural tube defects
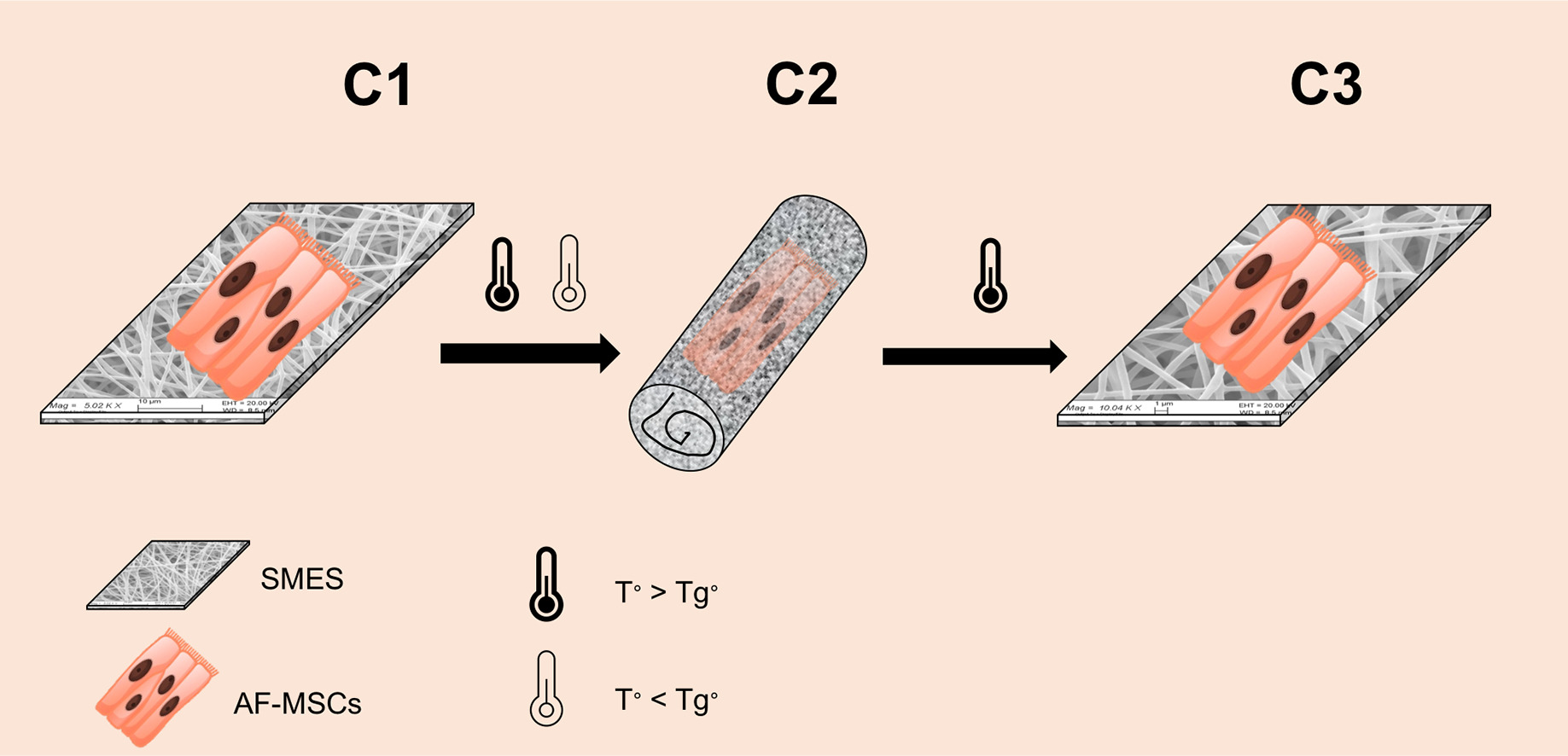
Neural tube defects (NTDs) represent the second most common cause of congenital malformations in the children. Aim of the work is the development of a shape memory engineered scaffold (SMES) focused to potentially improve Myelomeningocele (most common type of spina bifida defect) repair in fetus. Copolymer poly-L-lactideco-ε-caprolactone (PLA-PCL) 70:30 M ratio, due to its glass transition temperature (Tg◦) close to physiologic temperature (32–42 ◦C) was used to produce electrospun scaffolds that were engineered with MSCs from amniotic fluid. The engineered scaffolds were rolled up and then underwent a cycle of high (T◦ > Tg◦) and low temperature (T◦ < Tg◦) in order to induce solid status change from rubbery to glassy and fix their rolled shape. The scaffolds were characterized for the shape memory parameters Rf% (ability to fix new temperature induced shape) and Rr% (ability to recover the primary shape). Biological characterization included cell viability % determination by MTT test, cytofluorimetry and microscope analysis for DAPI stained and Live-Dead Assay. Scaffold degradation test was performed in amniotic fluid and mechanical properties of electrospun scaffold were evaluated up to 4 months incubation in amniotic fluid simulated in vivo conditions. The preliminary and innovative results obtained from this work permit to consider this SMES a good shape memory material (Rf% =79 ± 5.2; Rr% = 98 ± 3.1) and suitable support for MSCs proliferation.